Osteoarthritis (arthrosis) of the hip joint is a chronic and progressive pathology in which degenerative-dystrophic processes occur in the area of the joints of the pelvic bones. To be more precise, there is a destruction of the hyaline cartilage that lines the femoral head and the acetabulum, the surfaces of the pelvic bones that are in contact with each other.
The second name of the pathology is coxarthrosis of the hip joints.
Osteoarthritis of the hip joints: features of the disease
Most of the time, first-hand knowledge of what coxarthrosis is is for elderly people, especially women, who are at risk of developing pathology after 45 years. This selective appearance of the pathology comes from the specifics of the structure of the female pelvic bones, as well as their direct participation in the process of childbirth. In men, osteoarthritis of the hip joints (coxarthrosis) mainly occurs after age 65.
An important role in the pathogenesis of coxarthrosis is played by the body's natural aging, when the most stressed joints of the bones begin to collapse.
In addition, the disease can be triggered by various infectious, traumatic and non-inflammatory diseases, their combination. Initially, arthrosis manifests itself as pain and decreased activity of movements in the pelvic region, but its consequences become more serious - the affected limb is shortened.
Disease classification
The types of osteoarthritis of the hip joint depend on the characteristics of its development and the cause of its occurrence. Post-traumatic osteoarthritis of the hip joint is often present - it appears after an injury. The classification also includes the following types of osteoarthritis:
- Dysplastic - due to dysplasia that started in childhood but was not cured;
- Static - associated with an irregular load in the pelvic area, which happens with pathologies of the foot, knee, ankle;
- Post-infectious - appears after various inflammatory diseases;
- Primary chronic - develops in elderly people due to aging of the body.
Any type of disease can be called "deforming arthrosis of the hip joint", because the pathology leads to a violation of the shape and appearance of the pelvic joint of the bones.
In addition, the disease is divided into 3 degrees according to the severity of the changes, the symptoms of which are described below in the text.
Reasons for the development of osteoarthritis
Signs of coxarthrosis can appear even in the absence of obvious prerequisites, due to natural degenerative processes in the joint. It has a narrow gap, while supporting huge and constant loads, so it wears out sooner than others. Initially, blood circulation is disturbed in the tissues, so nutrients are delivered to the hyaline cartilage to a lesser extent. Metabolic processes are disturbed, cartilage dries up, cracks form in it. In addition, the joint surfaces are quickly worn out, destroyed - arthrosis of the hip joint progresses. Symptoms can appear even more quickly if the body is affected by several provoking factors:
- Any injury;
- Physical work, heavy sports;
- Spinal disorders, including curvature;
- flat foot;
- Arthritis in the context of an infectious process;
- Articular dysplasia transferred in childhood;
- Metabolic diseases;
- Overweight;
- Rheumatism and other autoimmune pathologies.
Against the background of the influence of such factors, the disease can develop much faster - after 30-40 years.
Symptoms of coxarthrosis
The signs of osteoarthritis of the hip joint largely depend on its degree. During the pathology, three degrees (stages) are distinguished:
- First degree. There are pains during physical overload - after a long walk, run, in connection with which there are painful and uncomfortable sensations in the pelvic region (pass after a short rest). The pain does not radiate to other parts of the leg. Deforming osteoarthritis of the 1st degree hip joint does not cause changes in gait, the muscles work at full capacity. At the end of the stage, small restrictions may appear in the movement of the legs;
- High school.Pain in arthrosis of the hip joint in this case becomes more pronounced. Pain appears with minimal exertion, discomfort is present at night after a day's work. There are pains at night, at rest. A popping, rubbing sensation in the joint. If a person walks for a long time, rocking movements can be noticed in gait. It becomes difficult to put on shoes, to take the foot to the side;
- Third degree.The work of the pelvic bones is seriously impaired (with primary osteoarthritis, both joints are affected, with other types, usually only one). The pain in the groin is constant, excruciating, knee-deep. The thigh muscles are atrophied. The leg gets shorter, so a person uses crutches and a cane to get around.
Later, ankylosis occurs, in which movement becomes impossible.
Disease diagnosis
What is coxarthrosis of the hip joint, what is its degree and how to treat the disease? All problems should be resolved after diagnosis. Despite the fact that the main method for making a diagnosis is radiography, the patient needs consultations with various specialists and close tests. This will help to find the cause of the disease and act on it. Thus, coxarthrosis can be triggered by osteochondrosis, flat feet, urological and gynecological infections, and their treatment will help to prevent bone joint destruction.
As for making an accurate diagnosis and defining the degree of arthrosis, all changes are perfectly visualized on an image - radiography or computed tomography (MRI):
- The first degree is a slight narrowing of the gap, the appearance of marginal osteophytes;
- Second degree - narrowing of the joint space to 50% of the norm, the appearance of osteophytes on the outer and inner sides of the gap, deformity of the head of the femur, often - the presence of inflammatory changes in the tissues near the bone joint;
- The third degree is a marked deformity of the joint, the presence of large osteophytes, zones of sclerosis.
Osteoarthritis treatment
Conservative treatment
Ointments, creams, tablets for osteoarthritis of the hip joint help only in the first stage of the disease. Medications can completely restore cartilage and it is important to start therapy at an early stage. Generally used NSAIDs, corticosteroids, chondroprotectors, hyaluronic acid-based drugs, muscle relaxants. They also practice massage, exercise therapy and therapeutic exercises.
In the second stage, it is necessary to connect physical therapy and mechanical methods of influencing the joint. These include exhaust, UHF, magnetotherapy, shock wave therapy, ultrasound, laser, indothermy, electrophoresis. Folk remedies for arthrosis of the hip joint, such as local drugs, are only of secondary importance, and the main method of therapy should be drugs.
Be sure to apply a diet for coxarthrosis of the hip joint, it is necessary to normalize metabolism and improve cartilage nutrition.
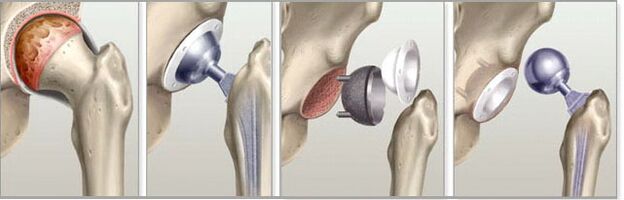
Endoprostheses for osteoarthritis
The third stage of the disease can only be treated surgically. The patient is recommended joint replacement surgery, or arthroplasty. The surgeon cuts the head off the femoral bone, inserts a metal pin into the cut, on which the artificial head is attached. After the operation, a long rehabilitation and exercise therapy is carried out, but the hip joint will fully function, and the doctor will be able to answer the patient in the affirmative to the question whether it is possible to squat with arthrosis of the hip joint.
Disease prevention
To prevent osteoarthritis of the hip joint, sports and a healthy lifestyle should come to the fore. It is impossible to overload the joints, but it is necessary to eliminate hypodynamia. Good for hiking, swimming, skiing, elliptical trainer. It's also important to lose weight and eat right.

Prevention of osteoarthritis of the hip joint is also based on early treatment of any bruises, injuries that affect the pelvis and spine. In childhood, all congenital joint pathologies must also be eliminated.
Answers to popular questions
- Who to contact with arthritis? The question of which doctor treats hip joint coxarthrosis does not have a definitive answer. Of course, initially it is recommended to contact a surgeon, traumatologist or orthopedist, which depends on the capabilities of the clinic. In specialized centers, an arthrologist deals with problems of the pelvic joints, but it is not always possible to find such a narrow specialist.
Depending on the cause of the disease, in the future, in parallel, you will have to apply and undergo treatment under the supervision of a rheumatologist, neurologist, infectologist and various other doctors;
- Can Arthritis Be Cured? This disease is chronic and it is impossible to eliminate it completely, mainly because the main cause is aging. But if you see a doctor when there is 1st degree osteoarthritis of the hip joint, you can cure all existing changes and prevent rapid progression. In subsequent stages, it is possible to stop and correct all existing pathological changes and live normally due to regular courses of therapy. Only arthroplasty can save the joint from arthrosis, but it also has several disadvantages - from the need for periodic replacement of the prosthesis to postoperative complications - pain, thrombosis, infection;
- When are local therapies sufficient and in what cases can a visit to the doctor be avoided? Any ointments can only slightly improve blood microcirculation in the joint area and also relieve pain, but they have no therapeutic effect. In addition, this joint is located very deeply, which makes it difficult for active substances to penetrate. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor at any stage of the disease, regardless of the severity of the manifestations. Only at an early stage can the disease be stopped with "low blood" without surgery.
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint is a disabling pathology that makes a person crippled, preventing him from walking.
The only way to prevent these problems from developing is to start conservative therapy at stages 1-2 of the disease, not forgetting to take regular and thorough courses.


















